Climate change
What is climate change?
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns. Such shifts can be natural, due to changes in the sun’s activity or large volcanic eruptions. But since the 1800s, human activities have been the main driver of climate change, primarily due to the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. Burning fossil fuels generates greenhouse gas emissions that act like a blanket wrapped around the Earth, trapping the sun’s heat and raising temperatures (UN, 2023).
Greenhouse gases such as:
- carbon dioxide (CO2)
- methane (CH4)
- nitrous oxide (N2O)
- fluorinated gases (that come from refrigeration or aerosols)
- evaporated water (H2O)
all contribute to the greenhouse gas effect. When any of these are emitted in excess they offset the natural balances of our planet such as the carbon and water cycle.
Greenhouse effect
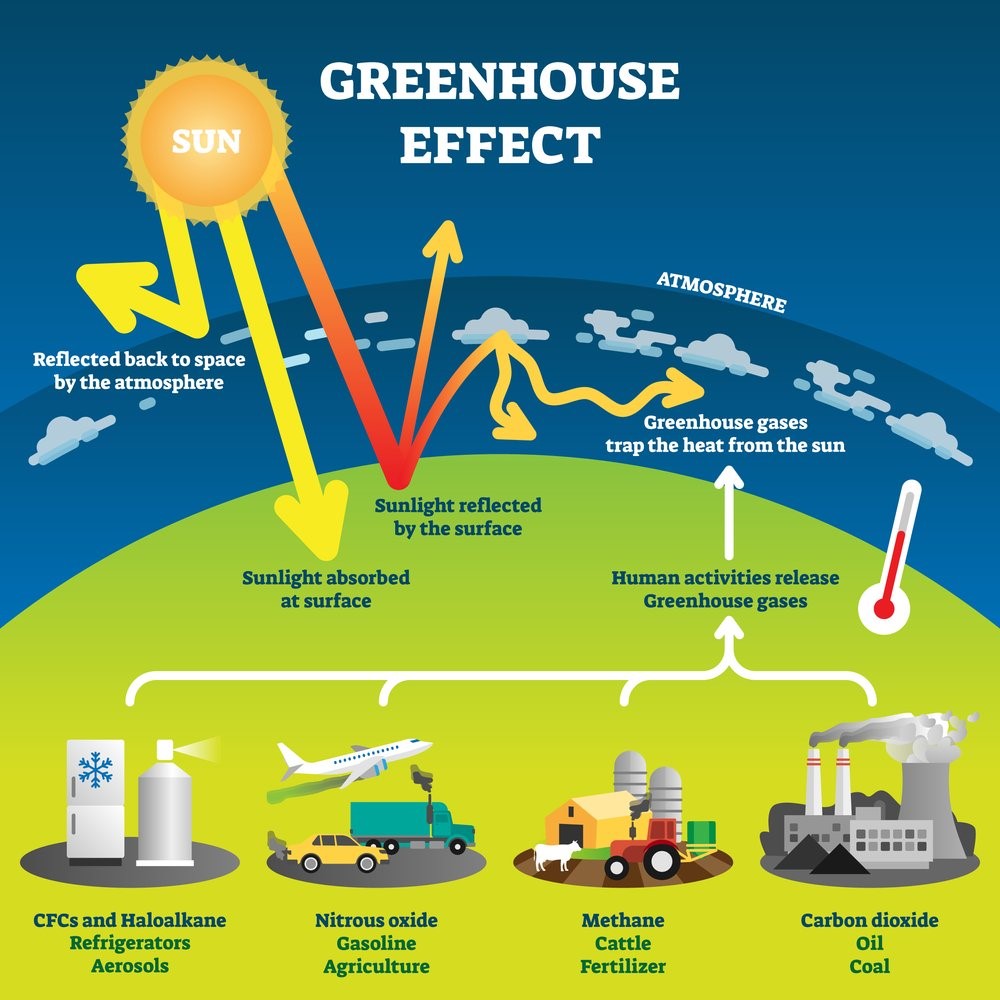
This image shows the earth, sun, atmosphere and sources of greenhouse gases.The sources located on the earth in the image portray:
- a fridge and aerosol can and reads “CFCs and haloalkane - refrigerators and aerosols”
- a plane car and HGV and reads “nitrous oxide - gasoline (petrol) and agriculture”
- a farm with cattle and a tractor and reads “methane - cattle and fertiliser”
- industry with smokestacks that reads “carbon dioxide - oil and coal”
There are arrows that lead from each source mentioned to the atmosphere to indicate human activities releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. There are arrows pointing towards the earth from the sun, the first goes towards the atmosphere but bounces back into space, indicating the sun’s rays being reflected back to space by the atmosphere, the second going straight to the earth through the atmosphere indicating sunlight being absorbed by the earth’s surface, and the third bouncing back at the surface level with three arrows bouncing off that point of contact with one leaving into space, and two others bouncing back from the atmosphere indicating that the sun’s rays escape back into space but also get trapped by the greenhouse gases released by human activity.
The main greenhouse gases that are causing climate change include carbon dioxide and methane. These come from using petrol for driving a car or coal for heating a building, for example. Clearing land and cutting down forests can also release carbon dioxide. Agriculture, oil and gas operations are major sources of methane emissions. Energy, industry, transport, buildings, agriculture and land use are among the main sectors causing greenhouse gases (UN, 2023).
The seriousness of climate change has been proven and communicated by the Intercontinental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) where 90 scientists from 40 countries concluded in 2018 that if there isn’t collective and effective climate action to limit global warming by 1.5 degrees Celsius by 2040 we will have surpassed the point of no return (IPCC, 2018).
Further information
Learn more about climate change on the United Nations web site.
Watch this video to learn more about greenhouse gases and their effect.
Learn more about the science and data related to climate change from the intercontinental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).

